01219245/cocos2d-js/Sprites2
- This is part of 01219245, 2nd semester 2557.
In this tutorial, we will recreate a clone of a wonderful Flappy Bird. Let's call it Flappy Dot (as our player would look like a dot). We will develop basic game mechanics in this tutorial. We will try to add special effects to the game in the next tutorial.
- Make sure you have completed Tutorial 100 on basic sprites.
Task breakdown
Before we start, make sure you know how this game works. You may want to try it for a bit. I guess many of your friends have it on their phones. This is how our game would look like:
As usual, let's start by thinking about the possible list of increments we would add to an empty project to get this game.
When you get your list, please see the steps that we plan to take here.
- Show the player on the screen.
- The player can jump and fall. (Implement player physics)
- Show a single pillar pair.
- Move the pillar pair across the screen.
- Let the pillar pair reappear.
- Check for player-pillar collision.
- Make the game with one pillar pair.
- Show more than one pillar pairs.
The player and its movement
You should start by creating a new Cocos-JS project.
cocos new -l js --no-native ชื่อโปรเจ็ค
This will create an example HelloWorld project. You should clean up the example by following instructions outlined in Tutorial 100.
Then, create a git repository at the project directory.
Creating the sprite
In this step, we shall create a sprite for the player, and show it in the middle of the screen.
Use a graphic editor to create an image for our player. The image should be of size 40 pixels x 40 pixels. Save the image as res/images/dot.png and try to make it look cute.
We shall create class Player as src/Player.js.
File: src/Player.js
var Player = cc.Sprite.extend({
ctor: function() {
this._super();
this.initWithFile( 'res/images/dot.png' );
}
});
We shall create the player in GameLayer.init. To do so add these lines:
File: src/GameLayer.js
this.player = new Player();
this.player.setPosition( new cc.Point( screenWidth / 2, screenHeight / 2 ) );
this.addChild( this.player );
this.player.scheduleUpdate();
Note that we use constants screenWidth and screenHight (which are 800 and 600, respectively). Don't forget to add this constant in main.js.
File: main.js
var screenWidth = 800; // add these two constants
var screenHeight = 600; //
cc.game.onStart = function(){
cc.view.adjustViewPort(true);
cc.view.setDesignResolutionSize(screenWidth, screenHeight, cc.ResolutionPolicy.SHOW_ALL); // use them here
// ...
};
cc.game.run();
Last step is to update configuration and resource files.
1. We need to add src/Player.js to the jsList in project.json.
File: project.json
// ...
"jsList" : [
"src/resource.js",
"src/GameLayer.js",
"src/Player.js"
]
// ...
2. Since we are using resource res/images/dot.png, we should preload it (so that we do not have to see empty screen when we start our program). Put the file name in src/resource.js (See more in section Technicalities: preloading of resources, later in this page.)
File: src/resource.js
var res = {
dot_png: 'res/images/dot.png'
};
// ...
Try to refresh the game. You should see your sprite in the middle of the screen.
Review of physics
You might forget all these, but if you want objects in your game to look and act a bit like real objects, you might have to recall stuffs you learned from mechanics.
Let's look at the basics. An object has a position, its position changes if it has non-zero velocity.
How can you change the player's position? Put something like this in Player.update:
this.setPosition( x, y );
If you want to apply the velocity, you can change the player position based on the velocity.
If there is an acceleration, the object's velocity also changes. The Sprite do not have velocity as its property, so we will add it. You can update the velocity based on the acceleration.
These properties (the position, the velocity, and the acceleration) all have directions. Sometimes, you see negative velocity; this means the object is moving in an opposite direction as the positive direction. We shall follow the standard co-ordinate system for Cocos2d, i.e., for the y-axis, we think of the direction as going upwards.
In Physics, everything is continuous. When writing games, we don't really need exact physics, so we can move objects in discrete steps. (In fact, method update is also called with parameter dt, the time period between this call and the last call, and you can use this to make your simulation more smooth.)
So the usual pseudo code for physics is as follows.
pos = pos + velocity; velocity = velocity + acceleration
Falling dot
To simulate the player falls, we should maintain the player's current velocity, so that we can make it falls as close as the real object.
Let's add this line that initialize property vy in Player.ctor:
File: src/Player.js
this.vy = 15;
You may wonder why we put 15 here. It is just pure guess at this point. However, when you write games, you might want to try various possible values and pick the best one (i.e., the one that make the game fun).
The update method changes the player's position
File: src/Player.js
update: function( dt ) {
var pos = this.getPosition();
this.setPosition( new cc.Point( pos.x, pos.y + this.vy ) );
this.vy += -1;
}
Note that we update this.vy at the end of update. The constant -1 is the acceleration. The parameter dt represents delta time; we do not use it for now.
Try to run the program. You should see the player falling.
While our program works, don't just rush to commit right away. Let's try to get rid of the magic numbers first, by defining them explicitly.
Add these line at the end of Player.js
File: src/Player.js
Player.G = -1;
Player.STARTING_VELOCITY = 15;
Then replace 15 and -1 in the code with the appropriate constants.
Jumping dot
Now, let's make the dot jumps. Let's add method Player.jump that set the velocity to some positive amount.
File: src/Player.js
jump: function() {
this.vy = Player.JUMPING_VELOCITY;
}
Also, add this constant after the class is defined in the .extend block.
File: src/Player.js
Player.JUMPING_VELOCITY = 15;
To jump, we have to call player.jump() in an appropriate time. We will response to keyboard inputs. We shall follow the style we did in the last tutorial.
First, add these functions. Function addKeyboardHandler registers the event handlers: onKeyDown and onKeyUp.
File: src/GameLayer.js
addKeyboardHandlers: function() {
var self = this;
cc.eventManager.addListener({
event: cc.EventListener.KEYBOARD,
onKeyPressed : function( e ) {
self.onKeyDown( e );
},
onKeyReleased: function( e ) {
self.onKeyUp( e );
}
}, this);
},
onKeyDown: function( e ) {
},
onKeyUp: function( e ) {
}
Then, call addKeyboardHandlers in GameLayer.init
File: src/GameLayer.js
init: function() {
// ...
this.addKeyboardHandlers();
// ...
},
We will jump in any key input, so we shall modify onKeyDown as follows.
File: src/GameLayer.js
onKeyDown: function( e ) {
this.player.jump();
}
To test this increment, you will have to click on the game canvas, and then quickly hit on any key to get the dot jumping. Try a few times to see how the dot moves. You can adjust the jumping velocity to make the movement nice.
Game states
It won't be nice to have the user start clicking right away after the game loads. Therefore we shouldn't let the player move before the game actually starts. To do so, we will add a state to the game. How various objects interact depends on the game state. In this tutorial, we shall simply add a property state to GameLayer, and perform various events and update methods according to this state. We will learn a cleaner way later on.
For now, the game has 2 states: FRONT and STARTED. After the game loads, its state is FRONT. In this state, nothing moves, and after the user hit any keyboard, it changes its state to STARTED with the dot start to jump. The dot falls and jumps as usual in the STARTED state.
Let's add the constants for states after the class GameLayer is defined (i.e., at the end of extend call).
File: src/GameLayer.js
GameLayer.STATES = {
FRONT: 1,
STARTED: 2
};
With this, we can refer to states as GameLayer.STATES.FRONT and GameLayer.STATES.STARTED.
Initial state
We let property state of GameLayer keeps the current game state. We initialize the state in GameLayer.init:
File: src/GameLayer.js
this.state = GameLayer.STATES.FRONT;
State transition
Our game changes its state when the user hits the keyboard, we rewrite method onKeyDown to
File: src/GameLayer.js
onKeyDown: function( e ) {
if ( this.state == GameLayer.STATES.FRONT ) {
this.state = GameLayer.STATES.STARTED;
// <--- some code to tell the player to start falling (TO BE ADDED LATER)
}
if ( this.state == GameLayer.STATES.STARTED ) {
this.player.jump();
}
}
Note that in the code above, if the condition in the first if holds, you will also execute the body of the second if. Therefore, the two conditions are dependent. When the user first hits the key, we let the player starts and also jumps. However, if you don't look carefully, you might not notice the jump call because it is in the second if.
We might want to make it a bit clearly like this:
File: src/GameLayer.js
onKeyDown: function( e ) {
if ( this.state == GameLayer.STATES.FRONT ) {
this.state = GameLayer.STATES.STARTED;
// <--- some code to tell the player to start falling (TO BE ADDED LATER)
this.player.jump();
} else if ( this.state == GameLayer.STATES.STARTED ) {
this.player.jump();
}
}
Or, you may want to use switch statement.
Player's state
Now, the Player shouldn't fall until the game tells it to get started. We shall add a state to the Player as well. Initialize property started in Player.ctor:
File: src/Player.js
this.started = false;
Add method start to update this state.
File: src/Player.js
start: function() {
this.started = true;
}
Finally, we only perform position update when the player is started.
File: src/Player.js
update: function( dt ) {
if ( this.started ) {
// ... old update code here
}
}
We shall call
this.player.start() // <-- this is the code to tell the player to start falling.
in the onKeyDown method in GameLayer.
The pillar pair
In this section, we will implement a moving pair of opposing pillars. Let's call them a pillar pair. Clearly, we will use one or more sprites to represent it. Before we think about how to implement it, let's think about what we want from this thing: (1) we want to move the pillar pair and (2) we want to check if the dot hits the pillars.
There are basically two approaches for this.
1. Use 1 sprite with transparent background in the middle. 2. Use 2 sprites (one for the top pillar, another for the bottom pillar).
Both approaches are shown below.
Question: Can you think of the advantages and disadvantages for using each approach? Expand to see some of the possible advantages and disadvantages.
Using 1 sprite is easier to deal with. However, the space between two opposing pillars are fixed. Using 2 sprites gives flexibility but it might be hard to to deal with two objects. It might be even worse if we have to deal with many pillar pairs.
Here, we will try to get the best out of both approaches. We will use 2 sprites, but we shall combine them into one object.
The blue object in the figure above contains two red sprite objects. Specifically, we shall create a cc.Node object that contains two sprites.
Sprite images
Draw two images for the top and bottom pillars. Since we can place each pillar at different height, we should make the images large enough so that the other end of the pillar is still outside the screen. The figure below shows the sprites and the screen; the red border shows the screen boundary.
So let's create two images pillar-top.png and pillar-bottom.png, each of width 80 pixels and height 600 pixels. Save them in directory res/images.
Node class
Let's create class PillarPair in src/PillarPair.js. In its constructor, we create two sprites from the images we have just created. Then we add the sprites as the child of this Node.
File: src/PillarPair.js
var PillarPair = cc.Node.extend({
ctor: function() {
this._super();
this.topPillar = cc.Sprite.create( 'res/images/pillar-top.png' );
this.topPillar.setAnchorPoint( new cc.Point( 0.5, 0 ) );
this.topPillar.setPosition( new cc.Point( 0, 100 ) );
this.addChild( this.topPillar );
this.bottomPillar = cc.Sprite.create( 'res/images/pillar-bottom.png' );
this.bottomPillar.setAnchorPoint( new cc.Point( 0.5, 1 ) );
this.bottomPillar.setPosition( new cc.Point( 0, -100 ) );
this.addChild( this.bottomPillar );
}
}
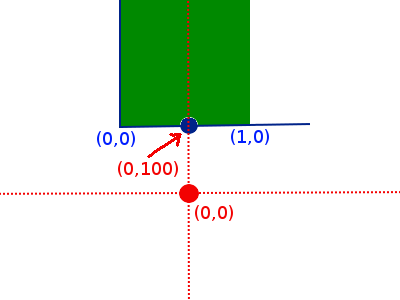
To put both sprites in the correct position relative to the position of the PillarPair, we set two properties of each sprite: the AnchorPoint and the Position. To understand this, consider the top pillar. We call
this.topPillar.setAnchorPoint( new cc.Point( 0.5, 0 ) );
to say that when we talk about the position of the top pillar, that position is the middle point (0.5) of the bottom (0) of the image (see Figure below, blue co-ordinates). For anchor points, the co-ordinate of the bottom-left corner of the sprite is (0,0) and the top-right corner is (1,1). Position (0.5,0) is the middle point of the bottom of the sprite.
We then call
this.topPillar.setPosition( new cc.Point( 0, 100 ) );
to place the top pillar at position (0, 100) relative to the position of the pillar: this means the top pillar is 100 pixels above the Node position (see Figure below, red co-ordinates).
Let's see if the pillars appear. Add file src/PillarPair.js to jsList in project.json. Then in GameLayer, let's add the code that create a PillarPair in GameLayer.init.
File: src/GameLayer.js
this.pillarPair = new PillarPair();
this.pillarPair.setPosition( new cc.Point( 700, 300 ) );
this.addChild( this.pillarPair );
Question: What is the width of the space between the top pillar and the bottom pillar?
200 pixels.
Moving the pillars
Let's add the code that move the pillars, PillarPair.update.
update: function( dt ) {
this.setPositionX( this.getPositionX() - 5 );
}
Then in GameLayer.init, add a line
this.pillarPair.scheduleUpdate();
after the PillarPair is created.
Technicalities: preloading of resources
If you runs the game a few times, you might notice that sometimes some pillar does not appear. This is because when we create the sprites, the images we want to use are not completely loaded. To avoid this problem, we will tell the Cocos2d-html5 library to load all our resources before starting our Scene.
Create file src/resource.js with the following content:
var g_resources = [
//image
{src: 'images/dot.png' },
{src: 'images/pillar-top.png' },
{src: 'images/pillar-bottom.png' }
//plist
//fnt
//tmx
//bgm
//effect
];
Note that this file lists all images that we want to use. There are other sections for other kinds of resources as well (plist, fnt, etc,...).
Add this file into file list in cocos2d.js:
appFiles:[
+ 'src/resource.js',
'src/GameLayer.js',
...
Notes: do not copy the green '+' signs or red '-' signs to your code; they are there to shows which lines are inserted and which lines are deleted. These are from git diff.
Finally, in the starting code in main.js, replace a call to runWithScene with a call to cc.LoaderScene.preload. (Replace the red line, with the green lines.)
director.setAnimationInterval( 1.0 / this.config[ 'frameRate' ] );
- director.runWithScene( new this.startScene() );
+ cc.LoaderScene.preload(g_resources, function () {
+ director.replaceScene( new this.startScene() );
+ }, this );
return true;
}
Now, when you start our game, you'll see the Cocos2d-html5 preloading start screen.
Moving the pillars after the game starts
Currently, we create the pillars right after the scene starts. We should synchronize this with the game state.
We will create the pillar pair often, so let's take the code for pillar creation out of GameLayer.init and place it in method createPillarPair:
createPillarPair: function() {
this.pillarPair = new PillarPair();
this.pillarPair.setPosition( new cc.Point( 900, 300 ) );
this.addChild( this.pillarPair );
this.pillarPair.scheduleUpdate();
}
In GameLayer.init, let's put this null initialization in place of the old pillar pair creation.
this.pillarPair = null;
Finally, let's call createPillarPair after the game state changes to GameLayer.STATES.STARTED in onKeyDown:
if ( this.state == GameLayer.STATES.FRONT ) {
this.state = GameLayer.STATES.STARTED;
this.createPillarPair();
this.player.start();
this.player.jump();
} else if ( ... ) {
// ...
}
Try the game to see if the pillar pair starts moving after we hit a keyboard.
The code for starting a new game currently lies in an event handler onKeyDown. This method will get longer and longer as we work on our game. So let's clean the method a bit. We shall extract the game initialization code into method startGame.
onKeyDown: function( e ) {
if ( this.state == GameLayer.STATES.FRONT ) {
this.startGame();
this.state = GameLayer.STATES.STARTED;
} else if ( ... ) {
// ...
}
},
// ...
startGame: function() {
this.createPillarPair();
this.player.start();
this.player.jump();
},
Test the code, and commit.
z-axis: Showing the player in front of the pillars
If you move the player through the pillars, you should notice that the pillars are drawn over the player. It would be better to have the player in front of the pillars. To do so, we assign the higher z co-ordinate to the player when we add the player to the GameLayer with method addChild.
this.player = new Player();
this.player.setPosition( new cc.Point( screenWidth / 2, screenHeight / 2 ) );
this.addChild( this.player, 1 );
Note that the default z co-ordinate is 0; so the z-co-ordinates of the pillars is lower than the player's.
Exercise: Reusing the pillars
In this game, our player will have to fly passing a lot of pillar pairs. However, we will not always create a new pillar pair. Instead, we shall reuse the old pillar pair that recently disappear on the left side of the screen.
EXERCISE: modify method PillarPair.update so that right after the pillar pair move outside the screen, it re-enter at the right side of the screen.